CBD effects • What are the benefits of CBD oil drops on the body and mind?
The potential effects of CBD are diverse. That’s why CBD and other cannabinoids from the hemp plant have been on the rise recently, especially in the past few years; hemp products have become increasingly popular. Cannabis has long been used for its potential therapeutic effects, yet hemp still carries a bad reputation. Unjustly, we believe.
Fortunately, it is possible to harness the benefits of cannabinoids legally and without psychoactive effects. All that’s needed is to use a CBD cannabis plant with a THC content (the psychoactive molecule) of less than 1%. These are known as EU industrial hemp varieties. The potential of CBD is enormous and is being researched more thoroughly. CBD side effects appear to be rare and mostly mild. Therefore, we will explore the effects of CBD oil and how you can use it for yourself.

Before starting to use CBD, you should always consult a doctor. The information in this article is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice for your health.
Table of contents for CBD effects
What is Cannabidiol anyway?
Before we delve deeper into how CBD works, knowing what CBD is is helpful.
CBD is short for cannabidiol. It is one of the many cannabinoids found in the cannabis Sativa plant. It is the most well-researched phytocannabinoid (plant cannabinoid) alongside THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) and is non-psychotropic. This means it does not induce “euphoria” or a “high” when taken into the body. This is the most significant difference from psychoactive marijuana. Instead, studies have established specific therapeutic effects. Examples include potential positive results in treating epilepsy, anxiety, and inflammation, which we will explore in more detail shortly.
How does CBD work in our body?
Raphael Mechoulam, an Israeli researcher considered the father of cannabis research, was the first to isolate the cannabinoids THC and CBD. He passed away in 2023. He conducted most of the studies related to cannabis and significantly influenced research in this area. In collaboration with a research group from the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, he discovered the endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system consists of CB1 and CB2 receptors, which are targeted by the body’s endocannabinoids and mediate the effects of cannabinoids.
This system is crucial for our body and primarily influences human homeostasis. It is involved in regulating various fundamental bodily functions. Those who have consumed THC-containing cannabis are familiar with the areas affected by the ECS. Hunger can occur, as well as fatigue. Red eyes and an increased pulse can also be consequences, illustrating some bodily functions influenced by the endocannabinoid system.
The Endocannabinoid system (ECS)
The ECS primarily consists of two different components. These are the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, targeted by the body’s endocannabinoids, which are cannabinoids produced by our body. Phytocannabinoids from the hemp plant can affect us because our bodies naturally have endocannabinoids. Phytocannabinoids mimic the structure of these endocannabinoids. The most famous representative of endocannabinoids produced by the body is anandamide, derived from Sanskrit and means “bliss” or “joy.” Anyone who has experienced the favorite runner’s high has likely felt the influence of anandamide.
According to the lock-and-key principle in biology, cannabinoids dock to endocannabinoid receptors. Cannabinoids have a particular shape that allows them to attach to cannabinoid receptors. They can act agonistically or antagonistically on the receptors. Agonistic action increases the activity of a receptor, while antagonistic action inhibits activity.
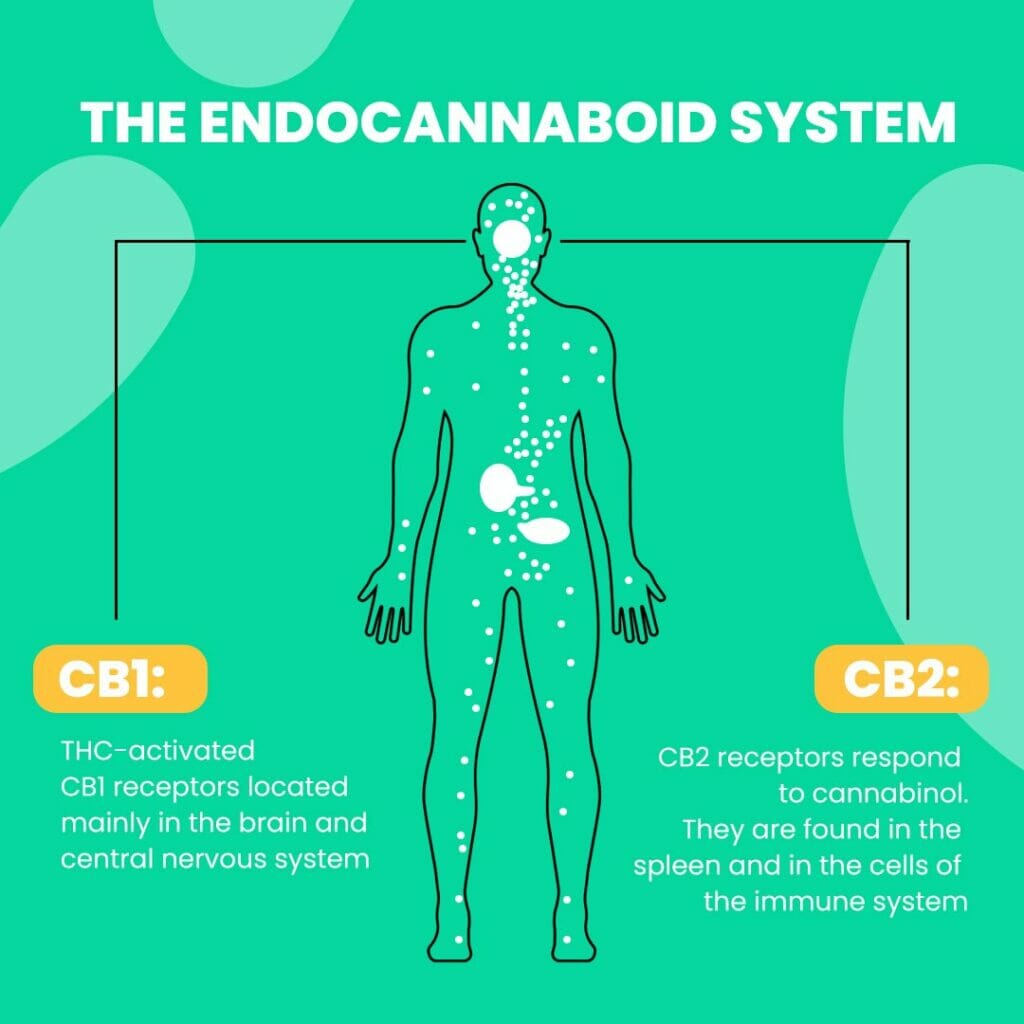
CB1 receptors
CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system. They are also in the spinal cord, macrophages, and mast cells. THC, for example, binds agonistically with a reference value of 1 to CB1 receptors. Since these receptors are more abundant in the brain and central nervous system, this leads to the psychoactive effect, making the user feel high. Synthetic cannabinoids are increasingly circulating on the cannabis black market, which can bind to CB1 receptors more strongly than with a reference value of 1. Values of 1000 or more are possible, making synthetic cannabinoids potentially life-threatening to your health.
CB2 receptors
CB2 receptors are primarily found in peripheral tissues, the digestive tract, and immune cells. They are also present in retinal cells, for example. CBD weakly activates (agonizes) CB2 receptors, which is why it is increasingly used for digestive complaints. Interestingly, CBD acts antagonistically on CB1 receptors, which can help alleviate the psychoactive effects of THC. By binding to CB1 receptors, CBD can reduce the binding of THC to these receptors, thereby mitigating the psychoactive effects of THC. Due to its antagonistic binding to CB1 receptors, CBD is not psychoactive.
The entourage effect
The entourage effect is also fascinating. This effect describes how the symbiotic action of cannabinoids and the hemp plant’s terpenes reveals new therapeutic properties. These properties cannot be achieved with cannabinoids or terpenes alone; they arise purely from symbiosis. Therefore, when it comes to cannabis flowers or extracts, the terpene profile is essential.
Cannabidiol effects: What does CBD help with?
If CBD hemp drops may be suitable to help with various symptoms, how exactly do they work? Let’s delve deeper into this. If you have such symptoms, you should have them diagnosed and treated by a doctor. Your health comes first! After that, it is advisable to consider CBD as an adjunct therapy in consultation with your doctor.
Scientific studies on Cannabidiol
Due to the effect of THC via the CB1 receptors, the following effects of (medical) cannabis are explained:
Appetite control, e.g., in chemotherapy-induced anorexia
CBD is often recommended for its anti-inflammatory properties. Since CB2 receptors are found on immune cells involved in inflammatory processes, this is probably the mechanism of action. Possible areas of application include rheumatism, inflammatory bowel disease, and arthritis. By inhibiting inflammation, CBD could indirectly alleviate pain because inflammation is reduced; therefore, fewer pain signals are transmitted.
By similar mechanisms, CBD could help with autoimmune diseases by regulating the excessive immune response. More research is needed for this. Two exciting application areas are CBD for epilepsy (especially in children) and the potential therapeutic properties of CBD for osteoporosis.
CBD for epilepsy

Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome are both forms of epilepsy. A toddler named Charlotte Figi first popularized CBD oil as an effective treatment. She increasingly suffered from epileptic seizures, and doctors could not provide her with the much-needed relief. Ultimately, the trial with CBD and the subsequent relief likely saved her life.
Since then, CBD oil’s anticonvulsant, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects have been extensively researched. This is especially true in treating epilepsy, such as the Dravet above syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
However, scientists are unsure exactly how CBD drops might work as an anticonvulsant. It may be due to CBD’s ability to reduce neural excitability. Furthermore, it may lead to a reduction in neural transmission by inhibiting adenosine reuptake. This chemical is traditionally considered an inhibitor of neural activity and a regulator of cerebral blood flow.
CBD for insomnia
Scientists believe that cannabis (with and without THC) could improve the sleep cycle or sleep quality. It has been found, for example, that CBD could help you fall asleep faster. Moreover, it could help maintain a better night’s sleep, meaning waking up less often during the night if CBD has been consumed beforehand. Unfortunately, large-scale clinical studies on sleep disorders are unavailable; most studies observe only small test groups of fewer than 100 people. Additionally, many studies were conducted with psychoactive THC-containing cannabis, not CBD, in isolation.

CBD against chronic pain and inflammation

When the body is injured, various types of compounds are released. They send pain signals but release compounds called prostaglandins, which are responsible for mediating inflammatory reactions. Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs work by inhibiting the release of these chemical compounds. CBD might achieve similar effects. We have already described its potential anti-inflammatory effects, likely mediated by CBD’s interaction with the CB2 receptors of immune cells.
How exactly CBD can help with pain needs further investigation. Medical cannabis containing THC is most commonly prescribed for chronic pain, with hemp preparations containing similar amounts of THC and CBD often being the best suited. Surveys of people with chronic pain have also shown that CBD positively affects patients. CBD can complement pain treatment, reducing the need for other analgesics such as opioids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen.
We look forward to more research focusing on CBD and its analgesic mechanisms.
The anxiolytic effect of CBD oil on the mind (against anxiety and stress)
Cannabidiol is not a cure for depression or anxiety, but evidence from scientific studies is steadily increasing.
A 2020 review published in the journal “Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research” summarizes all existing research on the anxiolytic effects of CBD oils. The authors conclude that CBD offers hopeful prospects for anxiolytic effects. However, the exact mechanisms are not described in detail. A similar tool to the one responsible for the antidepressant effects of CBD is conceivable.
CBD activates a serotonin receptor called 5-HT1A, inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and glutamate neurotransmitters. Antidepressants typically inhibit serotonin reuptake, preventing the reabsorption of the human happiness hormone serotonin and increasing blood levels. Depressive individuals often have a deficit in happiness hormones like serotonin or dopamine. Through this mechanism, CBD might potentially help with depression.

CBD in cancer

The potential therapeutic properties of CBD in cancer are far from adequately researched. Medical cannabis with THC is occasionally used adjunctively in cancer, for example, to treat weight loss and chronic pain, but CBD is not considered an active component in this context. Therefore, the takeaway from most studies in this area is that more research is needed.
CBD in women
There are often inadequate treatment options for numerous women’s diseases and menstrual complaints such as endometriosis or PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome). Those who venture into medical research on women’s complaints are often disappointed by the lack of research in this area. Therefore, it is all the more important to promote research into cannabis therapies for women’s diseases. While medical cannabis with THC is increasingly used for pain relief in endometriosis, CBD is also gaining popularity. Studies now suggest that CBD could help with endometriosis and PCOS. More research in this area is needed.
CBD in sex
Cannabis with THC is often consumed before sex. Consumers often report that sex feels more intense and different, adding fresh excitement to the bedroom. Unfortunately, there is limited research on CBD, so we must await further results.

CBD for skin and against acne

Since CBD has anti-inflammatory properties, scientists hypothesize it could also be effective against acne. A study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation concluded that CBD might prevent excessive sebum production, which contributes to the development of acne. For this purpose, CBD should be applied topically, such as in the form of a CBD cream.
Application and forms of CBD
Let’s explore the various applications and forms of cannabidiol (CBD) together. Here, we want to focus on the diverse range of CBD products that are becoming increasingly popular in the modern health scene. We can also discuss some aspects of effectiveness and regulatory acceptance that influence the use of CBD.
CBD products: a diverse range
From CBD oils to capsules, an impressive array of products is designed to make accessing this promising compound easier. CBD oil is the most popular form, efficiently dosed with its dropper. Consumers often praise their experiences with CBD drops. The range also includes body creams, salves, and even gummy bears or CBD lollipops for everyone’s taste and needs.
In addition, innovation in the form of cannabis sprays or hemp candies provides a new approach to CBD. Whether it’s a subtly scented spray for quick relief on the go or candies for a sweet treat in the evening, CBD showcases its versatility once again.
CBD products without proven effects: not medicines
Although many studies report the numerous benefits of CBD, including anti-inflammatory or calming properties, these effects are not considered clinically proven. It is important to note that many CBD products are sold without specific evidence of efficacy. According to Swiss law, it is not allowed to make health-related claims for products in this category. Most CBD products lack an indication or efficacy.
CBD products not approved as food
Despite their wide availability, CBD products have not been approved as regular dietary supplements. Consumers should keep this in mind and make their decisions accordingly. No matter how tempting it may be to snack on a “healthy” hemp candy or take a dose of “soothing” cannabis spray, these products do not fall into the same category as vitamins or mineral supplements. CBD products cannot be sold as food or dietary supplements in Switzerland. You can learn more about this in our article on the CBD oil ban.
How long do the effects of CBD drops last?
This depends on numerous factors. When consuming cannabinoids, tolerance can develop over time, which may require increasing doses. The mode of administration is also crucial. Oils administered sublingually or smoked cannabis flowers lead to a comparatively rapid increase in CBD levels in the blood. In contrast, oral preparations are absorbed into the bloodstream longer.
The following values are not based on research but on our and our customers’ experiences. More research is needed for precise information, as CBD’s blood concentration does not allow for exact conclusions about its effects.
Based on experience, sublingually administered or inhaled CBD can remain active in significant amounts for up to 5 hours after consumption. When orally ingested through digestion, it can be up to 10 hours, with CBD entering the bloodstream from digestion after 1 – 2 hours. You can learn more about the correct CBD dosage at the provided link.
FAQ: frequently asked questions about CBD effects
How fast does CBD work?
The time it takes for CBD to take effect varies significantly depending on the method of consumption. For oral consumption, it can take between 30 minutes to two hours for the results to be noticeable. In contrast, the effect is almost immediate when administered sublingually or through vaping. Other users who use CBD for long-lasting or chronic issues may only notice an effect after several days to weeks.
It’s important to note that various factors such as body weight, metabolism, and individual health conditions can also play a role. Therefore, it’s worth being patient and, if necessary, slowly increasing the dose to achieve the desired results. You should seek guidance from a doctor or physiotherapist when using CBD therapeutically.
How long does CBD stay in the body?
The exact duration that CBD remains in the body also varies depending on various factors. Depending on the consumption habits and metabolism, it can take about two to five days for the body to eliminate CBD.
Some studies suggest that with frequent consumption, it may take several weeks for cannabidiol to be eliminated. However, it’s not of significant concern because CBD in the blood or body doesn’t lead to disadvantages, whether in traffic or sports.
What are the known risks of CBD oils?
We have written a separate article about the potential side effects of CBD oil. Consuming high-quality CBD is essential so you know what’s in it. At uWeed, we test all products and send them to independent laboratories for quality control. A product can only be added to our range if the manufacturer’s information matches our laboratory results.
Please refer to the linked article above for a comprehensive overview of side effects. Side effects from CBD consumption are relatively rare. However, the following side effects are possible:
Nausea and loss of appetite
Dry mouth
Unpleasant feelings in the digestive tract
Headaches and migraines
Do hemp flowers cause a high?
A widespread misconception is the belief that hemp flowers inevitably lead to a high. This is due to the THC content in the plants, which is very low in industrial hemp varieties (usually below 0.2%). Therefore, it can be assumed that these varieties cannot cause a significant intoxication effect. The same applies to CBD products; despite their origin from the cannabis plant, the absence of substantial THC levels means they do not produce a “high” state. This is even true for the Swiss legal limit of 1% THC in cannabis plants.


